CSGO Chronicles: Unfolding the Gaming Universe
Dive into the latest news, tips, and trends in the world of Counter-Strike: Global Offensive.
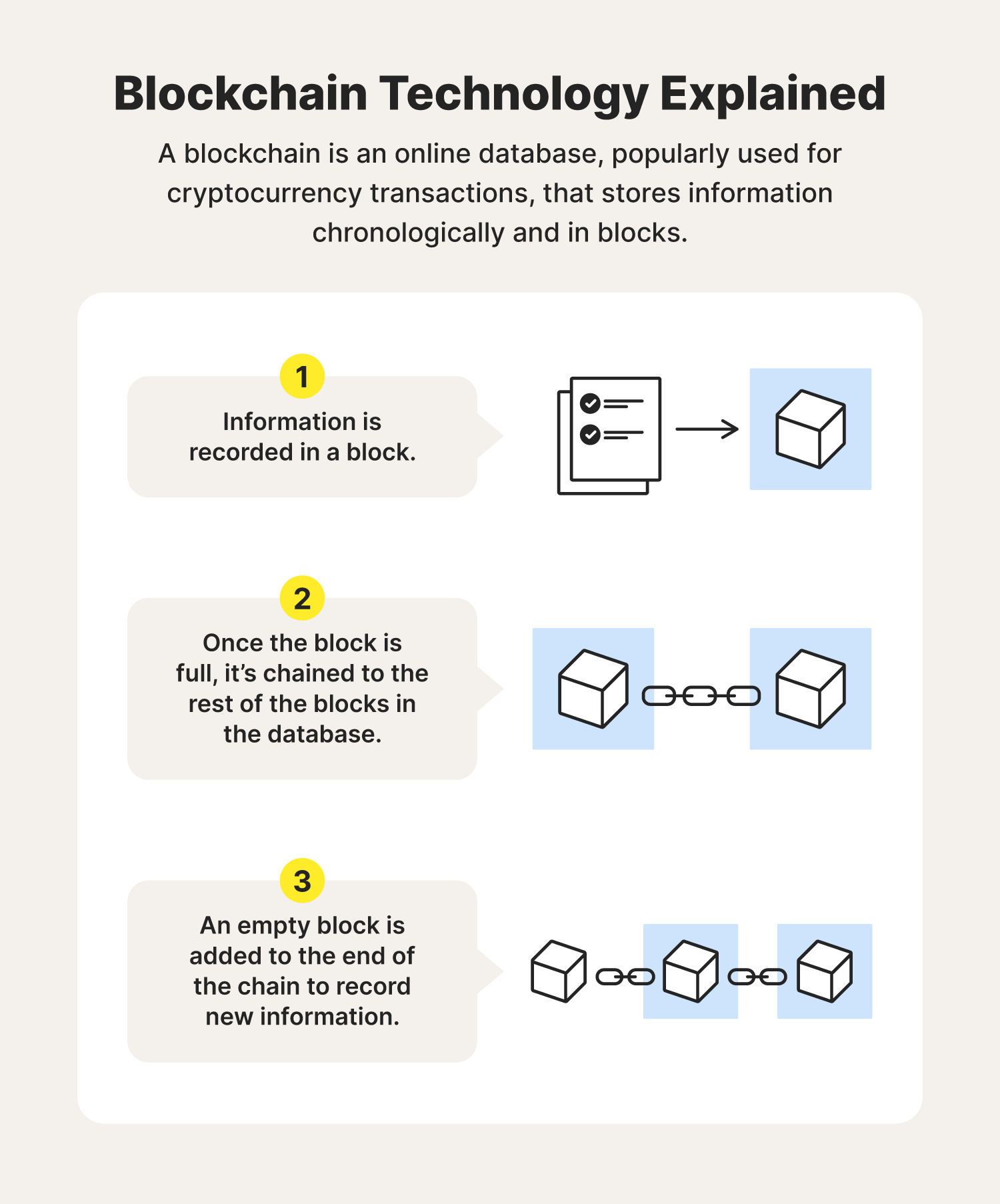
Blockchain: The Digital Playground for Trust Issues
Discover how blockchain transforms trust issues into opportunities in the digital age—your ultimate guide to this revolutionary technology!
How Blockchain Solves Trust Issues in the Digital Age
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, blockchain technology emerges as a game-changer in addressing the persistent issue of trust. Traditional systems heavily rely on intermediaries to validate transactions, which can often lead to disputes and fraudulent activities. By leveraging blockchain's decentralized nature, users can engage with one another directly, as the technology provides a transparent ledger that records all transactions securely. Each block in the chain is linked to the previous one, making it virtually tamper-proof, and this inherent security feature fosters greater confidence among participants.
Additionally, the trust afforded by blockchain extends beyond mere transaction security. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, revolutionize how agreements are executed in the digital age. For instance, in a business partnership, blockchain can ensure that all parties adhere to the agreed terms without the need for a central authority. This not only reduces the potential for conflicts but also accelerates the process. Ultimately, as more individuals and organizations adopt blockchain, the shift towards a more trustworthy digital ecosystem becomes increasingly apparent.
Exploring the Role of Smart Contracts in Enhancing Trust
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements where the terms of the contract are written directly into code. By leveraging blockchain technology, these contracts create a decentralized environment that enhances trust between parties. This transparency ensures that all transactions are verifiable and immutable, thus eliminating the need for intermediaries. As a result, businesses can streamline processes, reduce costs, and minimize the risk of fraud. The significance of smart contracts lies in their ability to automate enforcement and execution, allowing both parties to focus on their core operations without worrying about compliance.
Moreover, the implementation of smart contracts fosters a new level of accountability through its programmed logic. For instance, conditions stipulated in these contracts are automatically executed only when predetermined criteria are met, and any failure to fulfill these criteria can result in automatic penalties. This functionality not only strengthens the trust factor between parties but also motivates adherence to agreed-upon terms. As businesses increasingly adopt smart contracts in various industries—from supply chain management to real estate—they are discovering the transformative potential of enhancing trust and reliability in their operations.
Is Blockchain the Answer to Supply Chain Transparency Challenges?
The emergence of blockchain technology has sparked significant interest in addressing the longstanding challenges of transparency in supply chains. With its decentralized and immutable nature, blockchain provides a robust framework for tracking products as they move through various stages of production and distribution. This transparency can enhance accountability among stakeholders, as all transactions are recorded in a public ledger accessible to everyone involved in the supply chain, from manufacturers to consumers. Furthermore, by employing smart contracts, businesses can automate processes, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of fraud.
However, while blockchain offers promising solutions, it is essential to recognize that implementing this technology in supply chains is not without its challenges. One significant hurdle is the need for industry-wide standardization and collaboration among all participants to ensure that data is accurate and shared effectively. Additionally, the integration of blockchain technology with existing systems requires substantial investment in both infrastructure and training. Therefore, while blockchain has the potential to significantly improve supply chain transparency, its success will largely depend on the willingness of organizations to adapt and innovate collectively.