CSGO Chronicles: Unfolding the Gaming Universe
Dive into the latest news, tips, and trends in the world of Counter-Strike: Global Offensive.
5G: The Speedy Future That Will Leave Your Wi-Fi Jealous
Discover how 5G technology is revolutionizing connectivity and leaving traditional Wi-Fi in the dust. The future is here—are you ready?
How 5G Technology Works: A Deep Dive into Its Speed and Efficiency
Understanding how 5G technology works requires a look into its foundational principles and architecture. At its core, 5G operates through a series of networks that utilize millimeter waves, enhancing both speed and bandwidth. This new infrastructure is designed to support a significantly greater number of devices than previous generations of wireless technology. By employing advanced antenna technology, such as Massive MIMO, 5G can transmit data more efficiently over shorter frequencies, effectively reducing latency and allowing for peak data rates of up to 10 Gbps.
The efficiency of 5G technology is not merely rooted in speed; it also incorporates intelligent resource management and dynamic spectrum sharing. As the network dynamically reallocates resources based on user demand, it optimizes connectivity for a diverse range of applications, from streaming high-definition video to enabling the Internet of Things (IoT). This capability fundamentally transforms how we interact with technology, paving the way for innovations such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities. Thus, the evolution of 5G represents a significant leap forward in mobile communication, heralding a new era of connectivity.
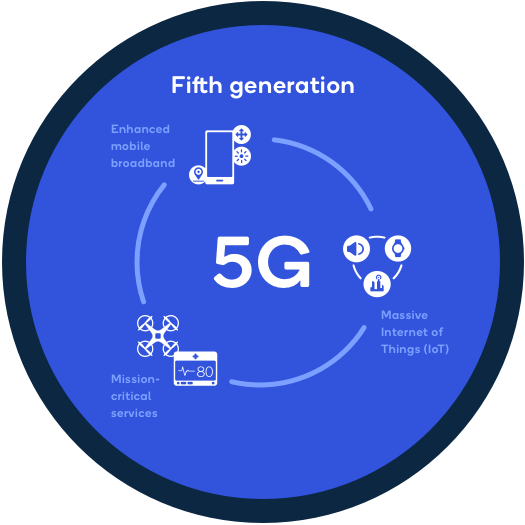
5G vs Wi-Fi: Which Is Faster and More Reliable?
5G and Wi-Fi are two powerful wireless technologies that offer high-speed internet connectivity, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Generally, 5G tends to provide faster speeds, especially in areas with good coverage. With maximum theoretical speeds reaching up to 10 Gbps, 5G aims to deliver fast and low-latency communication for a variety of applications, such as smart devices and real-time online gaming. In contrast, traditional Wi-Fi networks, particularly those operating on the latest Wi-Fi 6 standards, can achieve speeds of around 9.6 Gbps, though performance can be affected by range and interference from other electronic devices.
When it comes to reliability, each technology has its strengths and weaknesses. 5G offers wider coverage and can support a greater number of devices in densely populated areas, making it ideal for urban environments. However, its performance can vary significantly based on physical obstructions and network congestion. On the other hand, Wi-Fi is generally more reliable in indoor settings, especially in homes and offices, where users can connect to a stable router without interference from external factors. Ultimately, the choice between 5G and Wi-Fi may depend on specific needs, such as the requirement for mobility versus a stable home network.
The Future of Connectivity: What Does 5G Mean for Everyday Internet Users?
The advent of 5G technology is set to revolutionize the way everyday internet users experience connectivity. Unlike its predecessors, 5G offers vastly improved data speeds and lower latency, facilitating a smoother and more efficient online experience. For regular users, this means quicker downloads, uninterrupted streaming, and enhanced performance for applications that require real-time data transfer. With the potential to support thousands of devices per square kilometer, 5G lays the groundwork for smart homes, interconnected devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing seamless communication between your refrigerator, thermostat, and smartphone.
Moreover, the implementation of 5G is expected to widen access to high-speed internet, particularly in rural and underserved areas. This increased accessibility can bridge the digital divide, empowering more individuals to engage in remote work, online education, and telehealth services. As 5G technology continues to evolve, its impact will resonate through various sectors, promising innovations in augmented reality, virtual reality, and autonomous vehicles. Ultimately, for everyday internet users, 5G represents a leap towards a more connected and technologically advanced future.